Jaccard Cosine Similarity
Text Analytics - Jaccard and Cosine Similarity
Repository to showcase projects related to text analytics and Natural Language Processing (NLP)
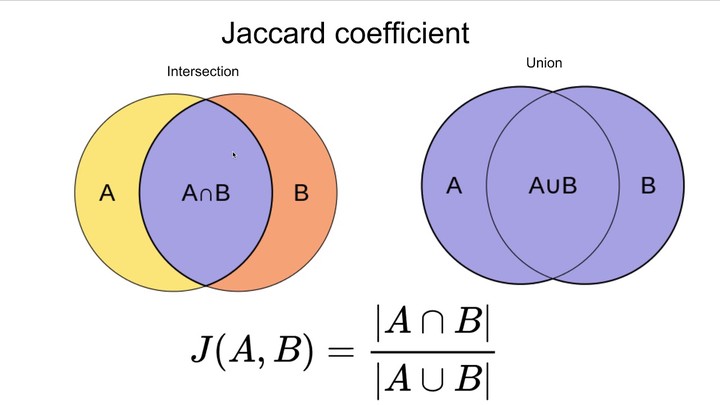
Jaccard Similarity: The Jaccard similarity index (sometimes called the Jaccard similarity coefficient) compares members for two sets to see which members are shared and which are distinct. It’s a measure of similarity for the two sets of data, with a range from 0% to 100%. The higher the percentage, the more similar the two populations.
#How to calculate: The formula to find the Index is:
Jaccard Index = (the number in both sets) / (the number in either set) * 100
The same formula in notation is: J(X,Y) = |X∩Y| / |X∪Y| In Steps, that’s:
1.Count the number of members which are shared between both sets. 2.Count the total number of members in both sets (shared and un-shared). 3.Divide the number of shared members (1) by the total number of members (2). 4.Multiply the number you found in (3) by 100.
Cosine Similarity: Cosine similarity measures the similarity between two vectors of an inner product space. It is measured by the cosine of the angle between two vectors and determines whether two vectors are pointing in roughly the same direction. Any document can be represented by thousands of attributes, each recording the frequency of a particular word (such as a keyword) or phrase in the document. Thus, each document is an object represented by what is called a term-frequency vector.
I used python function to calculate the text similarity rather than using the traditional way of calculating by using the formula.
Sources: https://www.statisticshowto.datasciencecentral.com/jaccard-index/
https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/computer-science/cosine-similarity